Future of IoT with 5G Technology
Internet of Things (IoT) is a new communication mode that will develop the current Internet and allow machine-to-machine (M2M) communication. Until recently, devices connected to the Internet were directly controlled by humans, mainly computers, tablets, and mobile phones. The Internet of Things will allow various devices to connect to the Internet, including sensors and smart tags.
This ubiquitous new era means that any device can be connected to the network anytime, anywhere. The world of information and communication technology has an additional dimension. This dimension means the connection from any person at any time and any place, and the definition extends to the connection of everything.
5G and IoT
The 5G technology will be an important component of the networked society. 5G will support huge numbers of connected devices and increase reliability in communication of mission critical applications. 5G will provide wireless connectivity for various applications such as smart homes, wearables, critical infrastructure, traffic safety/control, very high speed media delivery, industry processes etc.
IoT applications are well supported by LTE-M and NB-IoT based on 4G cellular networks but 5G will further enhance these Mobile IoT networks. 3GPP has incorporated LTE-M and NB-IoT into the 5G specifications, confirming their long-term status as part of future 5G standards. As the 5G technology evolves, the LPWAN (low power wide area networks) will become less complex and expensive. This provides a foundation for energy-efficient services.
5G benefits
The 5G will bring many benefits compared to earlier technologies in latency, speed and capacity. The benefits of 5G are summarized below with future possible roles:
Automotive and mobility
- High quality of services for navigation infotainment and other services due to large bandwidth.
- Larger bandwidth and low latency increases fuel efficiency and reduces drivers in platoons (Autonomous vehicle).
- Low latency and high bandwidth provides better remote vehicle maintenance which gives rise to new services and helps with cost savings.
Media and content
- Low latency and high bandwidth helps in transmitting high definition video in real time.
- With 5G, the AR/VR headset does not need advanced processing techniques, here the edge computing helps in processing large volumes of data.
- Low latency and high bandwidth 5G can support live broadcasting using smartphones and can give interactive and immersive VR experiences.
- 5G will enable enhanced customer experience for shopping and car parking with the use of VR.
Healthcare
- In operation theatres, the wired connection can be replaced by wireless connection by using 5G.
- Enhancing remote real-time diagnostics by delivering high quality video over 5G.
- 5G will help in real time diagnostics which provide high quality video streaming.
Manufacturing
- 5G enables efficient virtual control of machines due to the large bandwidth and low latency, this ultimately requires less processing power and less CPU for each floor.
- A large number of interconnected device can share information in real time, whichcan be transmitted to the cloud in real time and with high resolution.
- Inspection of sensors via Micro-robots and sharing the information in real time will help in cost reductions.
5G-IoT Architecture
This section introduces an architecture suitable for future IoT applications and services. The new architecture provides a more reliable, scalable and sustainable mobile IoT system than traditional IoT architectures. It provides a 5G-based architecture called 5G-IoT, with specifications that are modular, efficient, flexible, scalable, simple and responsive.
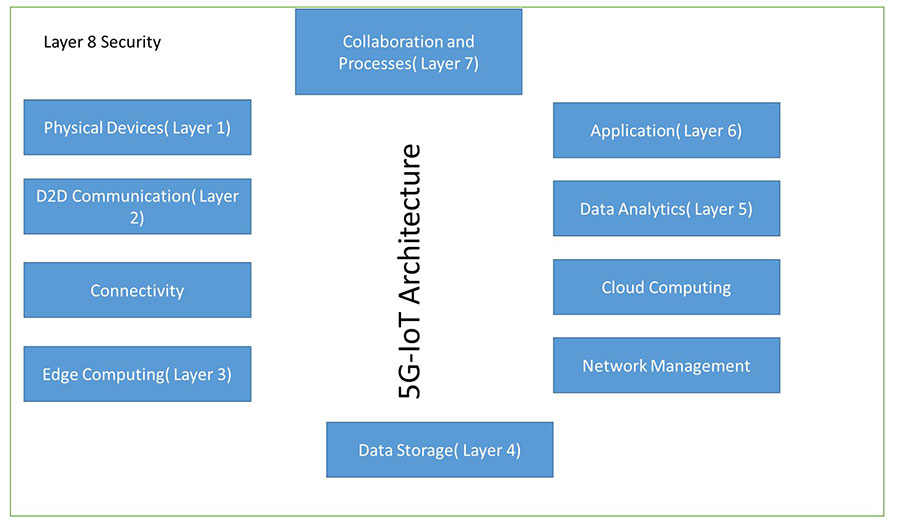
Figure: 5G-IoT Architecture
Physical device layer
This layer consists of wireless sensors, actuators, and controllers that are actually “things” of the IoT. Physical devices are a common layer across all architectures. Small components such as Nano chips are used in this layer to increase computing power and reduce energy consumption. Nano chips can generate large amounts of raw data which will be processed in the data analysis layer (Layer 7) suitable for big data.
Communication Layer
This layer consist of two sublayers.
Direct Device To Device (D2D) Communication Sub-Layer
Due to the increased computing power and intelligence, the physical device (node), has a unique identity and personality and generates its own data. To improve the performance and functionality of IoT systems, these devices must communicate with each other by forming a HetNet network. This lower layer uses the modern Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) communication protocol. A node can also choose a cluster head or cluster head( cluster head or Cluster head???). One of the key technologies that powers this infrastructure is millimeter waves. 5G is also another alternative technology in this lower layer that can improve D2D connectivity. 5G networks are great candidates for connecting to MTC ( Machine Type Communucation) devices. The high data rates of MTC and other high-quality media makes 5G-Plus-HetNet a powerful technical solution for the proposed 5G-IoT architecture.
Connectivity sub-layer
In this lower layer, devices are connected to the call center as BSs (Base station subsystem). It also sends and analyses data through the center via an intranet connection to the storage facility. Currently, this IoT sub-layer has some problems. It can only handle a limited number of device connections. In applications such as autonomous vehicles, data exchange does not apply to data types. High connection latency makes it difficult to process large amounts of data in real time. In the near future, 5G will significantly improve this foundation in terms of reliability, performance and agility.
Fog (Edge) computing Layer
This layer processes data from the node or its leaders to make decisions at the edge level. With the advent of 5G technology and mobile devices (such as smartphones), MEC (Multi-access Edge Computing) technology will become more powerful, address challenges and contribute significantly to this level.
Data storage layer
This layer contains the data storage unit, which stores the information obtained from the edge processing of the physical devices, as well as the original data. This layer requires special protection in terms of security, and must also respond to massive amounts of data and traffic from future applications.
Management Service layer
This layer consist of three sub-layers as follows
Network management Sub-Layer
Network management is changing the way devices and data centres communicate. The main technology of this subclass is WNFV (Wireless network function virtualization). WNFV can improve the quality of IoT architectures by simultaneously updating the network topology and communication protocol types such as 5G-IoT and ZigBee. Other technologies which are useful in these factories and smart cities include support for different types of data, support for many customers and requirements, and special features such as agility, flexibility, strong connectivity and low latency reliability. However, architectures based on 5G communication technology can meet the above requirements and provide the following features: Easy management, reliability, reconfiguration, advanced security, fast and easy troubleshooting, comprehensive coverage with a cost-effective 5G connectivity version. Also, most focus on 5G technology without paying much attention to other new technologies. In fact, the integration of 5G and IoT could allow many other technologies such as MTC and WNFV to contribute to the next-generation IoT architecture.
Cloud Computing Sub-Layer
This sub layer reprocesses data and information from on-board computations in the cloud and retrieves the information to be processed. The implementation of 5G technology will allow mobile devices to perform this type of calculation, called MCC, in real time. For example, computing activity is distributed in parallel between mobile devices, making IoT systems more efficient, reliable, scalable and faster.
Data Analytics Sub-Layer
This sub-level uses new data analysis methods to extract values (controllable information) from raw data. Improving big data algorithms improves data processing at this lower layer. Indeed, the role of this subcategory is likely to proliferate in the near future as the data collected by the integration of 5G and the Internet of Things increases.
Application Layer
At this level the program communicates with the previous level and data in standby mode, so no network speed is required. Through application control programs, vertical and mobile applications, business intelligence and analytics can transform vertical markets and business needs. In fact, the application layer allows businesses to do the right thing at the right time with the right data.
Collaboration and Processes Layer
The IoT system and the information from the first few layers is useless unless it generates behavior. Applications that run business logic empower people. People use applications and related data to meet their specific needs. Sometimes, multiple people use the same application for different purposes. In fact, people must be able to collaborate and communicate for the Internet of Things to work.
Security Layer
Like many architectures, this layer is considered a separate layer. In fact, this layer covers and protects all the previous layers, but each part (the intersection of this layer and another) has its own function. The security layer of the proposed architecture implies various security feature terms, including data encryption, user authentication, network access control, and cloud security. In addition, the security layer can also prevent and predict dangers and cyber-attacks, including forensics to detect and prevent the type of attack.
Conclusion
With the advancement of the Internet of Things, the flexibility of 5G is becoming more and more important for businesses. 5G technology supports critical connections with more precise performance requirements. The high reliability and low latency of 5G will enable autonomous vehicles, smart grids, advanced factory automation and other advanced applications. Supporting the realisation of the global vision of IoT by supporting a variety of connected devices with diversity and accessibility.






